Easy walking, long walks without fatigue even in the heels, beautiful ankles and hips you don’t want to hide from others - these are the benefits of healthy legs without signs of venous disease. Lifestyle and rhythm gradually change when a person neglects to prevent varicose veins.
This is true for both women and men. The disease develops in different ways, and the stage of varicose veins is always a matter of debate in medicine over the issue of patient identification. But you need to understand the classification so as not to miss the moment when the varicose veins can be treated without surgery.
The crux of the problem
Varicose veins are disorders of blood flow in the saphenous veins. Due to problems with the venous valves, which have to hold some of the blood to travel further to the heart, the plasma flows in the opposite direction and stagnates.
Pressure is unable to draw blood through the veins of the lower limbs, which can result in stretching of the walls. The legs gradually appear streaks of blue tones and a zigzag pattern, which is complemented by swelling and bulging at an advanced stage.
But the varicose veins are not immediately noticeable. The problem can progress without visual symptoms, so people who experience discomfort in their legs but cannot find protruding veins attribute the discomfort to fatigue.
Varicose veins do not occur in isolation. It is only a symptom of dysfunction of the circulatory system as a whole, which appears even at a young age. It is incorrect to consider varicose veins in the lower extremities as a sign of old age. Many girls around the age of 20 hide their legs under pants and long skirts because of varicose veins.
There are several possible causes of circulatory failure:
- Genetic inheritance from parents. If the mother (most often) or the father has problems with blood flowing from the legs to the heart, the children should have an examination and block the vascular and venous systems. But genetics does not always work if there is no motivating factor - a sedentary or sedentary lifestyle due to the peculiarities of the profession, unbalanced diet, complicated diseases;
- Ignoring the rules of technical break when used in certain work areas where the load on the legs is high but there is no movement (hairdresser, sales specialist, accountant, programmer, driver). Warming the feet every 30 minutes prevents blood stagnation;
- Some health problems affect blood vessels and veins - diabetes mellitus, heart disease, foot injuries, spine, obesity;
- Pregnancy in many women encourages the first symptoms of varicose veins. The embryo not only increases the weight of the expectant mother, which puts a strain on the legs, but also puts pressure on the pregnant woman’s internal organs and vital systems.
Varicose veins are severe signs of internal problems that have not yet been reported but require routine examination by at least one therapist.
Different stages of development of venous insufficiency
Although human veins are localized not only in the legs but throughout the body, varicose veins in the lower extremities are more common. Both women and men suffer from the disease, but a larger percentage of the beautiful half of the population.
There are several stages of varicose veins, which are classified according to their severity.The division is conditional, so the treating physician makes a diagnosis and knows which treatment regimen to prescribe to the patient for specific complaints.
There are several classifications of varicose veins among medical experts. The international community distinguishes seven stages of varicose veins, drawing a line within narrow symptoms. But in practice, varicose veins are diagnosed in 3 stages of disease progression:
- First stage (compensatory stage) - the deterioration of blood flow from the legs to the heart is determined by lifestyle or genetically, but the patient has time to restore the normal functioning of the venous valves. The symptoms of varicose veins are mild in the initial stages and are not taken seriously;
- Second degree (subcompensation) - there are visual signs of venous insufficiency that are difficult to confuse with other changes. The discomfort in the legs disappears after a long rest or constantly accompanies the person. At this stage, patients most often seek medical attention. Vascular and venous changes are significant, but it is possible to relieve tension and pain in the lower extremities;
- The third stage (decompensation) is the last stage of the varicose veins, when the thinned walls of the circulatory system begin to rupture from excess blood. The tissues of the skin are not fed and are destroyed. Skin ulcers develop that are difficult to treat. In some cases, in stage 3 of the varicose vein, bacteria join the ulcerous foci. Stabilizing a patient’s condition requires time, effort, and complex therapy.
The listed sections of the varicose vein are conditional divisions. Within certain groups of venous insufficiency, there is a mild, moderate, and severe degree of the disease, which is determined by the symptoms described by the patients at the reception. Based on the fact that the pathology of the veins is unique in each case, the line of transition from one stage to another is insignificant, especially in cases of 1 and 2 degrees.
Characteristics of the initial stage of the pathology
1 degree varicose veins are rarely diagnosed by a doctor because people do not go to the clinic when there is short-term edema or difficulty in the legs. Folk remedies help relieve fatigue, the swelling goes away on its own after sleeping or switching to high heels. The 1 degree varicose vein in many people only goes into another stage until old age if there is no provocative factor.
Changes in the vascular system occur not only in adults, but also in modern adolescents, who lack mobility and prefer computers, phones, and other devices to active leisure.
Only the arms and brain are trained, and the rest of the body does not change position for a long time. Blood circulation slows down, especially in the lower part of the skeleton. Bent knees, crushed muscles, blood vessels and blood vessels in the thighs, buttocks lead to stagnation.
Teenagers often complain of foot pain and cramps. In some cases, edema is seen, especially in case of overweight. Grade 1 varicose veins have no clear symptoms, but the initial stage has begun and its progression depends only on the attention of the children or their parents to themselves.
Teenage girls choose uncomfortable high-heeled shoes to attract attention. The pressure in the veins of the lower extremities increases and leads to an initial degree of pathology. The inability to stand and move in high heels deforms the foot, increases the load on the spine and bones of the feet, the hip joints. Curves negatively affect blood vessels because they compress.
The initial degree of varicose veins in young people is not disturbing because the symptoms disappear after rest or a little warm-up. The signs of a grade 1 varicose vein are:
- Heavy legs even without physical activity;
- Slight swelling in the afternoon when the foot is too small to fit into the shoe or when the edges noticeably dig into the skin. The symptom disappears in the morning when the legs are rested or a procedure is performed to relieve swelling and tension in the muscles - vertical position of the lower limbs, foot baths, massage, change of uncomfortable shoes;
- Short-term convulsions in rare cases.
In rare cases, grade 1 varicose veins show external signs of venous pathology - thin streaks of veins or vascular networks that are stressed due to decreased blood flow rates.
It is difficult to diagnose the initial stage of the pathology on its own, because the listed symptoms can be observed in other diseases, such as diabetes, kidney problems. For diagnosis and treatment, you should consult your doctor at the first signs of discomfort.
Varicose veins are not only localized in the legs, and the initial stage can be skipped if there is no change in the lower limbs.
Level 2 Features
The initial stage of venous pathology, in the absence of prophylaxis or therapy, enters the stage of subcompensation over time. Symptoms of grade 1 varicose veins are more common and last longer.
External changes appear on the skin - swollen veins or a large number of poker. Cramps occur both day and night, the patient feels pain and is unable to move his leg. Hardware examinations of the veins in the lower extremities reveal changes in the function of the valves.
The pressure in the blood vessels rises, but it is difficult to push the blood without closing the valves. Blood stagnation develops which appears in the form of blue lumps on the skin.
- Symptoms of stage 2 venous insufficiency are swelling that does not go away after rest and preventative procedures. Edema occurs because the blood is unable to rise in the veins and the hemodynamics deteriorate. The liquid part of the blood (plasma) begins to seep under the skin through the thinned walls of the veins and small blood vessels because the function of transport is impaired;
- Skin color changes due to poor circulation and nutrient intake. The cells of the epidermis take on a brown hue, gradually turning black. Inflammation develops and, as a result, the initial stage of ulcerative formations;
- Patients who see a doctor in stage 2 of the disease experience severe pain, muscle numbness and itchy skin. The symptoms are caused by a lack of proper nutrition in the cells of the epidermis.
The vascular undercompensation phase should not be considered hopeless if therapy is diagnosed and prescribed in a timely manner. If you notice one or more symptoms of grade 2 varicose veins, you will not be able to self-heal and listen to the benevolent. Only a doctor can help you cope with the problem.
Level 3 features
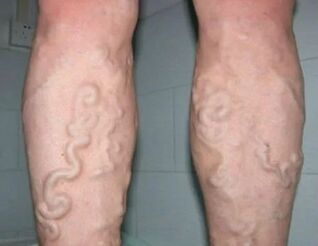
People achieve grade 3 venous insufficiency if they treat themselves carelessly and without due respect. The first stage of pathology rarely causes discomfort and alters quality of life, but Grade 2 venous insufficiency should not be overlooked in neglect of doctor visits and rehabilitation.
3-degree pathology is the most severe and dangerous because it forms trophic ulcers that do not heal even with medication. During the decompensation phase, the body exhausted its ability to keep the veins in working order.
The walls are stretched to the limit and thinned, there is a risk of cracking if damaged. Another problem with grade 3 varicose veins is thrombophlebitis - a blockage in a blood vessel, a blood clot that can become detached and lead to death.
Venous insufficiency reaches its final stage in extreme cases. The reasons for people’s attitudes toward themselves are not clear. It seems strange to endure pain, to feel discomfort because of aesthetic considerations, and not to be able to walk easily. Timely diagnosis of the problem and adherence to the doctor’s recommendations will not allow varicose veins to even cross stage 1 of the pathology.
After considering the varicose veins classification in detail, it is worth noting that venous insufficiency occurs in other parts of the body and internal organs. Such a problem is harder to spot, but when discomfort occurs in the legs, one can think of disturbances in venous blood flow elsewhere.
How to diagnose pathology
Get medical attention if you feel unwell for the first time. The diagnosis and treatment of venous insufficiency is handled by a phlebologist, but the first consultation can be obtained from a therapist.
- Visually examine the condition of the integument on the legs, the presence of orthopedic changes and other signs;
- Feeling not only the problem areas of the legs but also the groin and abdomen;
- Patients' complaints are heard;
- A detailed medical history is compiled in the form of a survey interview. The questions are aimed at identifying the cause that has become the starting point for the development of varicose veins;
- A referral for general blood and urine tests is needed to determine a patient's general health;
- Functional test to determine the degree of venous dilation (Schwarz, Perthes, single test);
- In case of varicose veins, a hardware examination is performed on the permeability of the veins and the condition of the venous valves - duplex ultrasound (DUS), plethysmography, phlebography, reovasography.

Following all measures necessary to diagnose venous insufficiency and quantify varicose veins, prevention, conservative therapy, treatment with alternative methods, and, in extreme cases, surgical intervention, laser pathology, are prescribed.
How to deal with varying degrees of venous dysfunction
The earlier you detect signs of a varicose vein, the easier and faster you can cope with the problem. The initial stage of the pathology can be completely eliminated without the use of drugs if you start prevention in time:
- Change your rhythm and lifestyle. Disruption of blood flow to the veins is often the cause of a sedentary or sedentary lifestyle for professional activity. Exercise should be added to increase hemodynamics and prevent high pressure in certain areas. In case of overweight, you should struggle with its normalization, but gradually;
- Choose comfortable and appropriate footwear. In the presence of orthopedic deformities, the shoe is selected taking this problem into account. High heels only for special occasions;
- Give up bad feelings that cause problems in the vascular system;
- Reduce weight if you are overweight and put extra strain on your legs;
- Choose the right exercise to help blood flow from your feet to your heart.
In the initial phase, the doctor prescribes venotonics, creams, tablets to reduce the load on the venous walls and restore their flexibility. The medical jersey should be individually designed to relieve tension in the legs.
If external signs appear that cause aesthetic discomfort, a special composition (sclerotherapy) is introduced into the vein, but this is rare at an early stage.
The second stage of venous insufficiency requires more attention to prevent the problem from turning into stage 3. The specificity of eliminating grade 2 pathology is similar to the treatment of varicose veins in the initial stage. Medication is prescribed to reduce the risk of blood clotting, reduce tissue swelling, and restore blood flow.

Surgical therapy for grade 2 varicose veins is used in the presence of obvious changes in the skin - convex veins, venous mesh, vascular system. Radiofrequency or laser therapy is performed in the treatment room. Sclerotherapy is also seen when an external defect disappears from the eye after the injection is placed in a problem area.
Compression garments are essential to improve blood flow and reduce foot stress.
How to treat grade 3 varicose veins when the condition of the veins and tissues is in a terrible state and the body is unable to correct the situation? The treatment is only surgical to prevent thrombosis, rupture of veins and restore hemodynamics throughout the body.
A phlebectomy procedure is usually performed - removal of the affected vessels. Surgery is performed with surgical instruments (classical method) or laser without a single incision (a modern method for treating grade 3 varicose veins).
The course of the disease is complicated by the development of ulcers that do not heal even with drug therapy. Therefore, you cannot be at this stage without a surgeon. After successful surgery, an individual course of medication, dressing, and medical canvas is selected.
In conclusion
Varicose veins are not a harmless cosmetic defect in the legs and other parts of the body, but a serious condition that, together with understanding, turns a person’s life into torture and constant walking in clinic offices.
The initial stage of venous insufficiency lies in the majority of the population, but diagnosis is rarely performed because people are unaware of the possible consequences.
If the professional activity involves a sedentary image or standing on a permanent foot, there are examples of relative pathology, you should take preventative measures and rule out the progression of the disease at an early stage. If you leave the problem unattended, you may not notice how your veins cause other pathologies.























